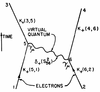
Single-Photon Source
A Single-Photon Source (SPS) is any system able to emit photons one by one. The typical measure of that is antibunching.
This problem is one of our research topics, as the particular case ($N=1$) of our multiphoton emission research.
We have provided a concept for a Perfect single photon source which, as opposed to the commonly accepted criterion $g^{(2)}(0)=0$, demands that $g^{(2)}(\tau)=0$ for all $\tau$ in a time gap. This has the unsuspected consequence that this produces bunching oscillations, which mark the onset of photon-ordering similarly to what happens when a gas liquefies, as we discuss in [arXiv:] where we further provide a mechanism for a full family of increasingly better SPS, with $g^{(2)}(\tau)$ function given by the elegant formula:
$$g^{(2)}_N(\tau) = 1 + \sum_{p=1}^{N-1} z_N^p \exp\big(- \gamma (1-z_N^p)\tau\big)$$
with
$$z_N\equiv\exp\left({2i\pi\over N}\right)$$
the $N$th roots of unity.
We have shown how two-photon suppression can be realized from admixing squeezed states with coherent states[1] and, more importantly, how such an understanding allows to realize joint subnatural-linewidth single-photon emission.[2] The underlying mechanism was generalized to a broad range of quantum emitters in Ref. [3]. This was confirmed experimentally by Hanschke et al.[4]
We also described the main and most widespread system for single-photon emission (a two-level system driven coherently and/or incoherently), as well as the loss of its antibunching, in Ref. [5].
Systems
With (what we believe is) first report:
- Atoms[6])
- Trapped ions
- quantum dots
- NV-centers[7]
- defects
- superconducting qubits
etc.
References
- ↑ Tuning photon statistics with coherent fields. E. Zubizarreta Casalengua, J. C. López Carreño, F. P. Laussy and E. del Valle in Phys. Rev. A 101:063824 (2020).
- ↑ Joint subnatural-linewidth and single-photon emission from resonance fluorescence. J. C. López Carreño, E. Zubizarreta Casalengua, F.P. Laussy and E. del Valle in Quantum Sci. Technol. 3:045001 (2018).
- ↑ Conventional and Unconventional Photon statistics. E. Zubizarreta Casalengua, J. C. López Carreño, F. P. Laussy and E. del Valle in Laser Photon. Rev. 14:1900279 (2020).
- ↑ Origin of Antibunching in Resonance Fluorescence. L. Hanschke, L. Schweickert, J. C. López Carreño, E. Schöll, K. D. Zeuner, T. Lettner, E. Zubizarreta Casalengua, M. Reindl, S. Filipe Covre da Silva, R. Trotta, J. J. Finley, A. Rastelli, E. del Valle, F. P. Laussy, V. Zwiller, K. Müller and K. D. Jöns in Phys. Rev. Lett. 125:170402 (2020).
- ↑ Loss of antibunching. J. C. López Carreño, E. Zubizarreta Casalengua, B. Silva, E. del Valle and F. P. Laussy in Phys. Rev. A 105:023724 (2022).
- ↑ Photon Antibunching in Resonance Fluorescence. H. J. Kimble, M. Dagenais and L. Mandel in Phys. Rev. Lett. 39:691 (1977).
- ↑ Stable Solid-State Source of Single Photons. C. Kurtsiefer, S. Mayer, P. Zarda and H. Weinfurter in Phys. Rev. Lett. 85:290 (2000).
| |||||||||||||