Coherent Oscillations in an Exciton-Polariton Josephson Junction. K. G. Lagoudakis, B. Pietka, M. Wouters, R. André and B. Deveaud-Plédran in Phys. Rev. Lett. 105:120403 (2010). What the paper says!?
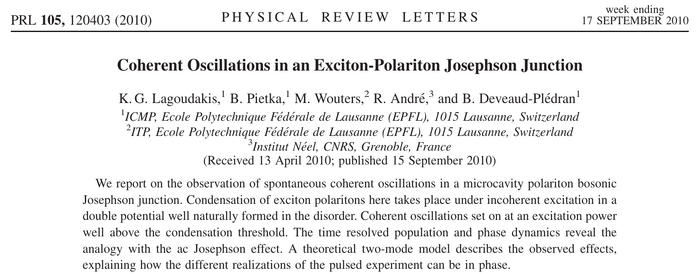
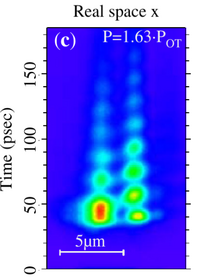
The Authors «investigate Josephson effects in a BJJ formed by two spatially separated condensates of exciton polaritons in a CdTe microcavity», i.e., polaritonic Josephson junctions, which they can image directly with a streak camera:
They are in the Rabi regime:
We therefore conclude that polariton-polariton interactions have a negligible effect on the oscillation dynamics and that our polaritonic BJJ is in the so-called Rabi regime.
The BJJ is in space with two traps:
The condensate pair is trapped in a naturally occurring disorder double potential well

The bulk of the paper is to explain why they see phase oscillations that are bounded, which they explain as a result of averaging over various realizations, which is also the reason why they don't see oscillations below a given threshold ($P_\mathrm{OT}$, probably for "Oscillations Threshold").

This would have been better plotted on the Bloch sphere.[1] They also did interferometry to measure the phase in spacetime. The reason of surviving averages has to do with a pinning of the phase due to asymmetries in the initial condition (their Eq. (4)) with simulations below and above the oscillation threshold shown in their Fig. 4. Note that although they say the phase shuold increase linearly, it actually decreases (nonlinearly).
Their take on what is most interesting:
the most remarkable phenomena are the ac and dc Josephson effects [4], the macroscopic quantum self-trapping, and the Josephson plasma oscillations [5]
Regarding the latter, they make an interesting clarification with those definitions:
A second question we can address with our model is whether our observations are rather related to the Josephson plasma oscillations or the ac Josephson effect. The latter effect is driven by the energy difference between the two potential minima, while the former originates from an initial condition that is different from the steady state.