
Contents
|
$\mathrm{\TeX}$ and $\mathrm{\LaTeX}$
$\mathrm{\TeX}$ is one of the masterpieces of Don Knuth.
It is the uppercase version of $\tau\epsilon\chi$, a Greek word for Tech, which is how $\mathrm{\TeX}$ should be pronounced (!?).
At some point in the early 2000, I switched to $\mathrm{\LaTeX}$ for convenience, and almost exclusively use the latter now.
Equations
Alignment
Splitting equations within an aligned set can be done as followed~[1]:
\begin{align}
a &= \begin{aligned}[t]
&b + c + d +\\
&c + e + f + g + h + i
\end{aligned}\\
k &= \begin{aligned}[t]
&l + m + n\\
&+ o + p + q
\end{aligned}
\end{align}
|
\begin{align} a &= \begin{aligned}[t] &b + c + d +\\ &c + e + f + g + h + i \end{aligned}\\ k &= \begin{aligned}[t] &l + m + n\\ &+ o + p + q \end{aligned} \end{align} |
To align equations as if in a table (?!), one can use [2] This is to integrate $\int x\sin(k\pi x)dx$ by parts.
\begin{align}
u&=x & v&=-\frac{1}{k\pi}\cos(k\pi x)\\
u'&=1 & v'&=\sin(k\pi x)
\end{align}
|
\begin{align} u&=x & v&=-\frac{1}{k\pi}\cos(k\pi x)\\ u'&=1 & v'&=\sin(k\pi x) \end{align} |
To gather equations (from the Wolverhampton Lectures on Physics on Mathematics):
\begin{gather}
\mathbb{R}^n\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_g\atop m\times n]{g}\mathbb{R}^m\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_f\atop l\times m]{f}\mathbb{R}^l\\
\mathbb{R}^n\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_{f\circ g}\atop l\times n]{f\circ g}\mathbb{R}^l
\end{gather}
\begin{gather} \mathbb{R}^n\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_g\atop m\times n]{g}\mathbb{R}^m\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_f\atop l\times m]{f}\mathbb{R}^l\\ \mathbb{R}^n\xrightarrow[\mathbf{J}_{f\circ g}\atop l\times n]{f\circ g}\mathbb{R}^l \end{gather}
International accents
We try to write your name properly when we quote it. Here are the most common glyphs and the code needed to do so:
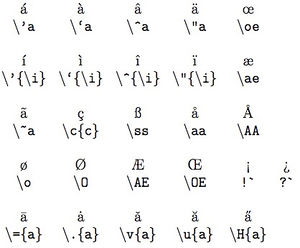
$?`$Does this work?
and a more comprehensive list of accentuated characters.
Fonts
See Will Robertson preambles to use different fontsets.
Shortcuts
Useful shortcuts, include:
- \to instead of \rightarrow for $\to$ (also mapsto for $\mapsto$)
- \gets instead of \leftarrow for $\gets$.
- \implies instead of \Longrightarrow for $\implies$ (is there a shortcut for \Rightarrow which is the prettier $\Rightarrow$?)
Colors
Using the package
\usepackage[svgnames]{xcolor}
One can then use \textcolor{red}{this is red} or \color{red} to turn everything red (until next escape).
The predefined colors are:
black, blue, brown, cyan, darkgray, gray, green, lightgray, lime, magenta, olive, orange, pink, purple, red, teal, violet, white, yellow.
but some of them are horrible! like this horrible #00ff00 pure green (so-called lime) (what it calls lime is even less visible). The svgnames gives access to about 150 additional, and pretty, colors. Use capitals letters. Here are the most useful with a short name:
|
|
|
And here are all of them.
Unicode
Unicode can be supported (at least to some extent) with
\usepackage[mathletters]{ucs}
\usepackage[utf8x]{inputenc}
It works at least for the Greek letters.
Formatting
- Wrapping figures in text: [3]
Lists
- To change spacing between items, put after \begin{itemize}:
\addtolength{\itemsep}{-0.5\baselineskip}
- To change the starting value of an enumerate list (enumii if it's a sublist):
\begin{enumerate}
\setcounter{enumi}{4}
\item fifth element
\end{enumerate}
- To change the type of numbering:
\renewcommand{\theenumi}{\Roman{enumi}} \renewcommand{\theenumi}{\roman{enumi}}
- To change enumeration (with square brackets, parentheses, etc.): (see [4])
\usepackage{enumitem}% http://ctan.org/pkg/enumitem \begin{document} \begin{enumerate}[label={[\arabic*]}] \item First item \item Second item \item \ldots \item Last item \end{enumerate} \end{document}
Footnotes
There is a $\mathrm{\LaTeX}$ package, footmisc, that is useful for manipulating footnote formatting.
- Spacing between footnotes:
%\footnotesep is the space between footnotes:
\setlength{\footnotesep}{-0.5\baselineskip}
%\footins is the space between the text body and the footnotes:
\setlength{\skip\footins}{1cm}
- To use footnotes to feature reference-style annotations, that is, with no subscripts and with enclosing brackets [1], add in the preamble:
\makeatletter
\renewcommand{\@makefnmark}
%{\@textsuperscript{\textit{\tiny{\@thefnmark}}}}
{[\@thefnmark]}
\renewcommand\@makefntext[1]{%
\parindent 1em
\noindent
[\@thefnmark]\enspace #1}
\makeatother
(I left, commented, the original definition of the footnote).
Geometry
\usepackage[a4paper, total={6in, 8in}]{geometry}
To use "infinite"-width page to accommodate single-line long formulas, use the package standalone:
\documentclass[border=1in]{standalone}
\usepackage{lipsum}
\begin{document}
\begin{minipage}{66cm}
\lipsum[1-150]
\end{minipage}
\end{document}
This is, unfortunately, incompatible with the RevTeX package or amsmath tools in general. In this case one has to use geometry:
\documentclass[preview, border=1cm]{standalone}
\usepackage[total={50cm, 20cm}]{geometry}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\begin{document}
\begin{subequations}
\begin{align}
\sigma_1^{(1)}&=\sqrt{\frac{\gamma_a^4+2\gamma_a^3\Gamma+6\gamma_a^2\Gamma^2+2\gamma_a\Gamma^3+\Gamma ^4}{\gamma_a^2\Gamma^2(\gamma_a+\Gamma)^2}}\\
...
\end{align}
\end{subequations}
\end{document}

Units
We use the siunitx package:
\usepackage{siunitx}
It'd take \SI{500}{\milli\second} to understand.
Please write \SI{10}{\micro\meter} and not 10$\mu\mathrm{m}$
There is also a SIUnits which is however deprecated [7]. Sometimes it comes in handy, for instance when you want to add non-numerical inputs (though siunitx should be able to allow that as well).
To write inverse unit, use \per:
shows the PL emission of a \SI{3}{\micro\meter} wire, where one can
observe the splitting between the two first confined subbands, the
polarization splitting, and the crossing of the X and Y (labelled TE
and TM here) polarized lines around \SI{2.6}{\per\micro\meter},
whereas the value given by the formula above is
\SI{2.1}{\per\micro\meter}.

The powers of ten can be counter-$\mathrm{\LaTeX}$-intuitive:
with a density of $\SI{e-3}{\per\square\micro\meter}$
If you do not use SI units, then omit the slash:
repetition rate of SI{3}{gb/s}
(that would be giga-bits per seconds).
Symbols
To use \mathbb{1} produce the "identity" ![]() , use the package
, use the package
\usepackage{bbold}
Bold letters
Greek letters can be typeset with the bm package
\usepackage{bm}
which produce $\bm{\alpha}$, $\bm{\beta}$, $\bm{\gamma}$ as![]() .
.
Line numbering
It's useful to number profusely manuscripts of which you are discussing every line. Package lineno does that.
\usepackage{lineno}
\linenumbers

It may have a hard time cohabiting with amsmath, however. It appears that if you include this monstrosity somewhere in your preamble, it'll perform well enough for line-dropping with your co-authors:
\newcommand*\patchAmsMathEnvironmentForLineno[1]{%
\expandafter\let\csname old#1\expandafter\endcsname\csname #1\endcsname
\expandafter\let\csname oldend#1\expandafter\endcsname\csname end#1\endcsname
\renewenvironment{#1}%
{\linenomath\csname old#1\endcsname}%
{\csname oldend#1\endcsname\endlinenomath}}%
\newcommand*\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno[1]{%
\patchAmsMathEnvironmentForLineno{#1}%
\patchAmsMathEnvironmentForLineno{#1*}}%
\AtBeginDocument{%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{equation}%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{align}%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{flalign}%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{alignat}%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{gather}%
\patchBothAmsMathEnvironmentsForLineno{multline}%
}
texmf
Local files (such as laussy.sty) are to be put in a local version of the texmf directory (texmf stands for $\mathrm{\TeX}$ and Metafont). This is to be declared to the system as follows:
texhash /home/laussy/comp/texmf
lualatex
To use fonts such as Arial or Colibri, one can use lualatex. This requires the installation of:
sudo apt install texlive-luatex
as well as the installation of the fonts themselves. Note that still within $\mathrm{\LaTeX}$, one can use the package helvet to use a look-alike free font (Nimbus Sans font):
\usepackage{helvet}
\renewcommand{\familydefault}{\sfdefault}
but if you want the real proprietary font, you have to commit your soul to some endt-user license agreement which is however easily done through
which is however easily done through
sudo apt install ttf-mscorefonts-installer
If the fonts you want are not part of this, such as calibri, then you need to find it elsewhere (for instance, here), and then you can declare your choice of font as follows (un/comment as needed; you may have to declare the exact path to the files as shown below):
\usepackage{fontspec}
%\setmainfont{Arial}
%\setmainfont{calibri.ttf}
\setmainfont[Path=/usr/local/share/fonts/c/,
BoldItalicFont=calibriz.ttf,
BoldFont =calibrib.ttf,
ItalicFont =calibrii.ttf]{calibri.ttf}
Compilation
Use texfot to get rid of the flood of output generated by compilation and retain only the warnings:
texfot pdflatex Microcavities.tex
See also
- BibTeX to manage references.
- laussy.sty my personal $\mathrm{\TeX}$ definitions.
Links
On this Web
Elsewhere on the Internet
- The Comprehensive $\LaTeX$ Symbol List of November 2015 (331 pages of glyphs).