Integrated quantum polariton interferometry. D. Nigro, V. D’Ambrosio, D. Sanvitto and D. Gerace in Commun. Phys. 5:34 (2022). What the paper says!?

The Authors lay down the foundations for quantum computation with polaritons (or strongly-interacting [Kerr type] propagating particles).
They first propose a nonlinear HOM interferometer, which is basically a case with interactions spoiling the HOM dip (their Fig. 4), so much it is spoilt can tell you how much particles interact. Diminution of the HOM dip could be due to many other factors, though, and maximizing it is usually the intent, so the interest here seems moderate.
They encode their logical basis as follows:
which leads to the following operators from either Free Propagation or bringing them closer into an Interacting Region:
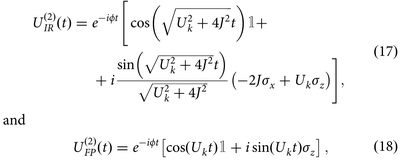
Then they consider a two-hopping region scheme:
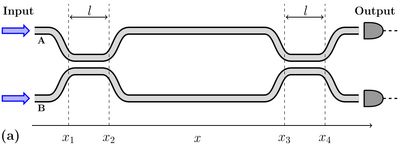
which, for interactions large enough, result in a square root of SWAP gate at small times (or small propagation distances). They show this through the two types of correlations (cross and auto of the two paths), which they find analytically (their Eq. (25)).
This is for single-rail encoding, so demands the ability to "not measure" a polariton (or measure vacuum).
There is a nice reference list of recent papers on various applications.
novel ideas aimed at developing deterministic quantum gates based on effective pho tonic interactions have been put forward$^{35-37}$.
References
- ↑ Controlled-Phase Gate Using Dynamically Coupled Cavities and Optical Nonlinearities. M. Heuck, K. Jacobs and D. R. Englund in Phys. Rev. Lett. 124:160501 (2020).
- ↑ Photon-Photon Quantum Phase Gate in a Photonic Molecule with $\chi^{(2)}$ Nonlinearity. M. Li, Y. Zhang, H. X. Tang, C. Dong and G. GuoC. Zou in Phys. Rev. Appl. 13:044013 (2020).